Six Sigma – Overview, Principles, and Methodology

What Is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a process improvement methodology that is used in many different industries. It was developed by Motorola in 1986 and has since become one of the most popular business strategies for improving processes, products, and services. The main aim of Six Sigma is to improve the quality of processes and increase customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma encourages businesses to focus on reducing variation, eliminating defects, and defining measurable goals to optimize their performance. It works by breaking down each process into individual tasks or activities that can be measured. Through this approach, organizations are able to identify areas where they can make improvements while also monitoring performance over time. This helps them reduce costs while providing high quality products or services that meet customers’ needs. Additionally, Six Sigma provides organizations with a structured framework for identifying opportunities for process improvement and executing successful projects through data-driven decisions.To learn more about Six Sigma, write to us or join our Six Sigma Training
Six Sigma Principles
The five main tenets of Six Sigma are as follows:
1. Customer focus
Customer focus is a fundamental part of any successful business, and is a cornerstone of Six Sigma methodology. Implementing Six Sigma principles can help businesses develop an effective customer-centric approach to their processes, leading to improved performance and better customer satisfaction. A major benefit that comes with using Six Sigma in this way is its ability to identify the root cause of problem areas, allowing for targeted solutions that can be quickly applied for maximum effect.
Six Sigma’s methodology focuses on understanding what customers value from their interactions with the company, enabling organizations to create or enhance products and services that provide true value to their customers. It also helps companies analyze customer feedback data more effectively in order to identify problems or areas for improvement before they have a chance to become major issues. By proactively addressing these issues, businesses are better positioned to exceed customer expectations and build loyalty among their client base.
2. Examine the value chain and identify the issue
The Value Chain is a process that examines the flow of products and services that create value for customers. Understanding the value chain helps companies identify opportunities for cost savings, revenue generation and quality improvement. For organizations committed to Six Sigma, the value chain can be even more valuable as they strive to reduce defects and increase customer satisfaction.
Organizations using Six Sigma will use the value chain analysis to identify issues in their processes that lead to defects or dissatisfied customers. This analysis allows them to pinpoint problem areas quickly without having to sift through all of their process steps. By doing so, Six Sigma practitioners can take corrective actions faster and with less disruption than trying a trial-and-error approach.
3. Get rid of flaws and outliers
Six Sigma is a set of principles used to improve processes and eliminate defects in any industry. It’s also known as the 3 Sigma Method, and it’s been used for decades by businesses around the world. Eliminating defects and outliers is one of the primary elements of Six Sigma, as it can help to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
The goal of Six Sigma is to identify problems that cause defects or outliers in a process, such as sub-optimal quality control measures or inadequate training. Defects are identified based on data analysis to determine the root cause of failure in each step of the process. Once these issues have been identified, changes can be made to ensure that all products meet customer expectations without fail. These changes can include better quality control methods or improved training so employees understand how their actions affect product quality.
4. Include interested parties.
Six Sigma is an important business process that many organizations rely on to streamline operations and reduce costs. For successful implementation, it is essential to involve stakeholders in all phases of the project. This article will discuss the importance of involving stakeholders during the implementation of Six Sigma projects.
One reason why stakeholders should be involved in a Six Sigma project is that they can provide valuable input regarding what needs to be done and how it should be done. Stakeholders have a vested interest in the success of any given project and are usually invested in its outcome. They can also give feedback about whether or not certain activities are effective, helping to ensure that any changes made will actually improve processes and lead to overall efficiency gains.
In addition, involving stakeholders from different departments or functions allows for better cross-functional collaboration within an organization.
5. A responsive and adaptable system
Six Sigma is a business strategy that has become popular over the past few decades. The goal of Six Sigma is to reduce defects and increase efficiency for businesses, allowing them to provide better customer service and maximize profits. With this in mind, a flexible and responsive system can help organizations meet these goals.
A flexible and responsive system allows an organization to adapt quickly to changing customer needs, respond effectively to market conditions or technological advances, and create new products or services more quickly. It also provides a framework for managing data in real-time so that decisions can be made based on the most up-to-date information. This flexibility helps companies stay ahead of their competition while still delivering quality results. Additionally, by having a more streamlined process with fewer errors, organizations are able to save time and money while improving overall efficiency.
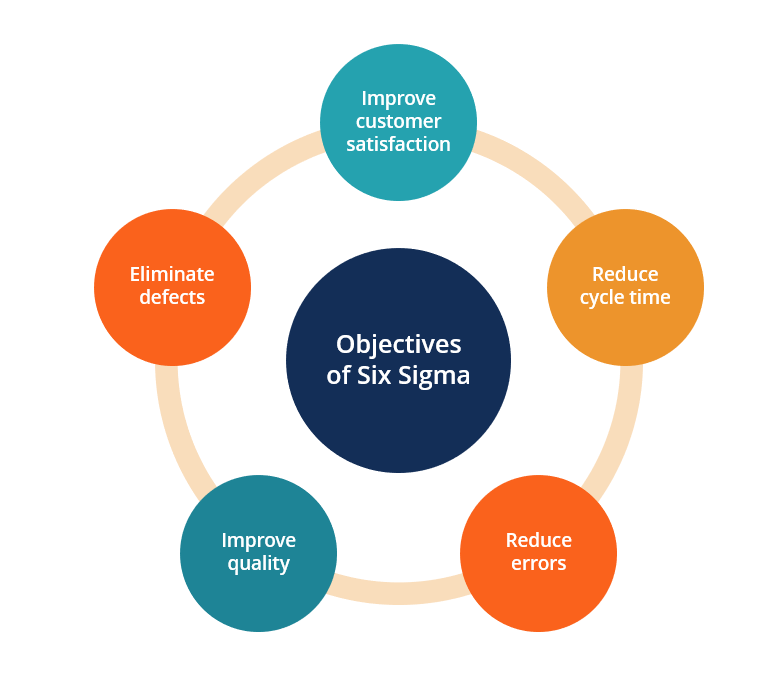
Six Sigma Methodology
The two primary Six Sigma methodologies, which are applied in various business settings, are as follows:
DMAIC
DMAIC is a data-driven methodology for optimising and enhancing current corporate structures and procedures. It is a successful technique for managing controlled change. Following is a list of the five DMAIC phases, each of which includes tools and tasks to aid in determining the ultimate answer.
- Define the issue and the project’s objectives.
- Measure each component of the current process in great detail.
- Analyze data to identify a process’s primary problem
- Enhance the existing procedure
- future procedure implementation under your control
DMADV
DMADV concentrates on the creation of completely original methods, goods, or services. It is employed when new procedures must be designed since current processes, even after improvement, still fail to meet the needs of the client. There are five stages to it:
- Specify the project’s, item’s, or service’s objectives.
- Analyze the core capabilities of a process and a product.
- Develop design alternatives based on data analysis, and then choose the best one.
- Create the best option that was chosen, then test the prototype.
- Verify the design’s efficacy through many simulations and a pilot project.
In conclusion,Six Sigma is a powerful tool for businesses to use in order to improve their processes and become more efficient. It provides organizations with the opportunity to set targets and monitor progress as they strive for maximum efficiency and continually improve their operations. Implementing Six Sigma requires an organizational commitment, dedicated resources and committed leadership. However, its benefits far outweigh the time and money spent implementing it. Organizations that have adopted Six Sigma have seen vast improvements in customer satisfaction, cost savings, and overall process quality.